Let’s make apps on mruby/c for M5Stack(ESP32)
TechEmbedded, English, ESP32, M5Stack, mruby, mruby/c
This article comes from 2nd M5Stack user meeting.
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1jTYKZZlFtwx6KfR7aCY7NBsK0vqvqM8u3NedsVozIl4/mobilepresent?slide=id.p
My intention
I think M5Stack is an awesome product because following functionalities are put into one small case!
- WiFi
- Display (with good APIs)
- Speaker
So far I have made some consoles, but it is not easy way (of course I’ve had a lot of fun).
M5Stack is just what I wanted.
Environment
It’s OK to use C to implement some small project for me.
But sometime I hear following comments from Web SW engineers.
- I’m interested in making electric things
- But I cannot do soldering
- I don’t know C. (maybe I don’t want to use…)
I want to introduce an alternative way to them.
The alternative way is mruby?
Sometime I see MicroPython about this topic. I think this is going to be the most common way for this purpose recently. M5Stack is officially support it on M5Clould.
https://micropython.org/
But I like Ruby!
So I was interested in mruby some years ago1.
The core of M5Stack is ESP32, ESP32 has 520KB SRAM. This is quite big amount of RAM in the world of micro processor.
We can use mruby on ESP32.
https://github.com/mruby-esp32/mruby-esp32
(I would also like to contribute it.)
But it is possibly not enough if we want to write big mruby code. mruby requires more than N*100KB RAM. (I don’t have solid data. Somebody says it’s more than 400KB.)
therefore I had been finding any solutions. Unfortunately I lost several years because of busyness in my job.
In my understanding, Yamane san struggle against this topic. I was encouraged by her.
“mruby can be more lightweight”
Why mruby/c?
Today I found mruby/c!
This is focussing on micro controller to reduce RAM usage as much as possible.
https://github.com/mrubyc/mrubyc
They say;
Comparison between mruby and mruby/c
| mruby/c | mruby | |
|---|---|---|
| memory size | < 40KB | < 400KB |
| main target | one-chip microprocessors | general embedded software |
This can work with less than 40KB RAM! That’s great for me.
Let’s implement something to M5Stack using it.
What I did
Everytime we need to wait for writing bin to FROM on the target board. It’s annoying everybody in the world. Even we use mruby, we need to wait for writing “bytecode”.
If it works like as irb, it’s nice to check micro controller behavior quickly.
Then I modified mirb in order to send byte code to M5Stack.
Normal mirb
Normal mirb works as a following figure.
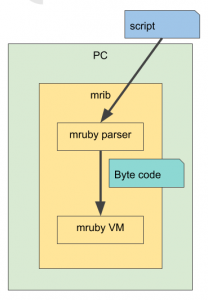
Important points are in main() like,
parser->s = utf8;
parser->send = utf8 + strlen(utf8);
parser->lineno = cxt->lineno;
mrb_parser_parse(parser, cxt);
code_block_open = is_code_block_open(parser);
mrb_utf8_free(utf8);
This is the parser of mruby. The parser recognize each line of mruby script.
/* generate bytecode */
struct RProc *proc = mrb_generate_code(mrb, parser);
This is generating mruby byte code for each proc.
result = mrb_vm_run(mrb,
proc,
mrb_top_self(mrb),
stack_keep);
stack_keep = proc->body.irep->nlocals;
This is throwing each proc to mruby VM. When the function returns, the stack register will be kept.
My idea
My idea works as a following figure.
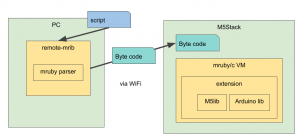
I added a mrbgem, the name is mruby-bin-rmirb. (“rmirb” means “remote-mirb”)
This is copied from mirb.
In rmirb, rmirb_send_irep() is called in stead of mrb_vm_run();
In rmirb_send_irep(), each proc is sent to M5Stack by a socket. I used mrb_dump_irep() to make a parsable byte-code since the proc is note bytecoded fully. This has some C-variables.
char* rmirb_send_irep(mrb_state *mrb, struct RProc *proc){
//create a message
int size=0;
unsigned char* msg =NULL;
rmirb_make_irep_msg(mrb,proc->body.irep,&size,&msg);
if(size==0){
return recv_buff;
}
//send a message
// header
// type: 2bytes
// message size: 2 bytes
unsigned char buff[4];
buff[0]=0xFF;
buff[1]=1;//1:irep 2:reset 3:exit
uint16_to_bin(size,&buff[2]);
//printf("%s:size=%d\\n",__func__,size);
int res = send(rmirb_socket,buff,4,MSG_NOSIGNAL);
if(res>0){
printf("socket error!\\n");
return NULL;
}
//irep body
res = send(rmirb_socket,msg,size,MSG_NOSIGNAL);
if(res>0){
printf("socket error!\\n");
return NULL;
}
free(msg);
return recv_buff;
}
void rmirb_make_irep_msg(mrb_state *mrb, mrb_irep *irep, int* size, unsigned char** msg){
uint8_t *bin = NULL;
size_t bin_size = 0;
uint8_t flags=0;
int result;
result = mrb_dump_irep(mrb, irep, flags, &bin, &bin_size);
if (result == MRB_DUMP_OK) {
int i=0;
/*
for(i=0;i<bin_size;i++){
printf("%02x ",bin[i]);
}
printf("\\n");
*/
*size = bin_size;
*msg = bin;
}else{
printf("irep dump error!\\n");
*size = 0;
}
}
Todo: Each byte code includes redundant sections. This should be removed.
a movie of current PoC implementation
Following source code has many bags as of now.
- rmirb source code
https://github.com/kishima/mruby/tree/rmirb
I will make a mrbgem repository. -
source code for M5Stack
https://github.com/kishima/mrubyc_for_ESP32_Arduino
This is included in mruby/c for ESP32 Arduino lib.
Need to enable “ENABLE_RMIRB” in “mrubyc_for_ESP32_Arduino.h”.
Future work
- Fix bugs
- Receive results from mruby/c VM.
- Implement binding C functions of M5Stack and ESP32 Arduino lib.
- Implement a function to download mruby bytecode via WiFi
- Reduce RAM usage more.
- Let’s write a book about mruby/c for “技術書典5”
-
This is a my old article in 2012. ↩
関連記事
直近の活動予定
直近の対外的な活動予定を記載しています。 今後のイベント (技術書、もう一冊書き ...
技術書典7でESP32とmruby関連の新刊出します
技術書典7もいよいよ明日になりました。サークル当選したので、今回も新刊出す予定で ...
独習mrubyバイトコード[GETIV]
OP_GETIV Arguments A: レジスタ番号 Bx: シンボル番号 ...
Wio LTEでmruby/cを動かすArduinoライブラリを作った
英語版はこちら。 先日、第60回 kawasaki.rbで↓のようなLTしてきま ...
技術書典6サークル参加と近況報告
しばらく忙しくて、更新の間が空いてしまいました。 技術書典6にサークル参加します ...
格安USBホストIC(CH559)を試す
簡単にUSBホスト機能を自作のプロジェクトに追加できる方法を知ったので紹介したい ...









Recent Comments